Trading and Investment Strategies
What is a trading strategy?
A trading method is simply a plan you follow when executing trades. There’s no single perfect approach to trading, so each method will largely rely on the trader’s profile and preferences.
Regardless of your approach to trading, setting up a plan is crucial – it outlines clear goals and can stop you from going off course due to emotion. Typically, you’ll desire to decide what you’re trading, how you’re going to trade it, and the factors at which you’ll enter and exit.
In the following chapter, we’ll get into a few examples of popular trading strategies.
What is portfolio management?
Portfolio management concerns itself with the introduction and handling of a collection of investments. The portfolio itself is a grouping of property – it ought to comprise some thing from Beanie Babies to real estate. If you’re completely trading cryptocurrencies, then it will in all likelihood be made up of some combination of Bitcoin and different digital coins and tokens.
Your first step is to think about your expectations for the portfolio. Are you searching for a basket of investments that will stay tremendously protected from volatility, or something riskier that may bring higher returns in the short term?
Putting some thought into how you prefer to manage your portfolio is notably beneficial. Some may pick a passive strategy – one where you leave your investments alone after you set them up. Others may want to take an active approach, where they constantly buy and sell assets to make profits.
What is risk management?
Managing risk is necessary to success in trading. This starts with the identification of the types of risk you may likely encounter:
Market risk: the potential losses you could encounter if the asset loses value.
Liquidity risk: the potential losses springing up from illiquid markets, where you cannot easily locate buyers for your assets.
Operational risk: the potential losses that stem from operational failures. These may additionally be due to human error, hardware/software failure, or intentional fraudulent habits by employees.
Systemic risk: the potential losses brought about by the failure of players in the enterprise you operate in, which affects all businesses in that sector. As was the case in 2008, the collapse of the Lehman Brothers had a cascading impact on worldwide financial systems.
As you can see, risk identification starts with the assets in your portfolio, however it should take into account both internal and external factors to be effective. Next, you’ll desire to assess these risks. How frequently are you possibly to encounter them? How severe are they?
By weighing up the risks and figuring out their feasible impact on your portfolio, you can rank them and increase appropriate strategies and responses. Systemic risk, for example, can be mitigated with diversification into exclusive investments, and market hazard can be lessened with the use of stop-losses.
Be sure to check out Financial Risk Explained and A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Risk Management.
What is day trading?
Day trading is a strategy that entails entering and exiting positions inside the same day. The term comes from legacy markets, referencing the reality that they’re only open for set durations throughout the day. Outside of those periods, day traders are not expected to keep any of their positions open.
Cryptocurrency markets, as you probably know, are not subject to opening or closing times. You can trade around the clock every day of the year. Still, day trading in the context of cryptocurrency tends to refer to a trading style where the dealer enters and exits positions in 24 hours.
In day trading, you’ll frequently rely on technical evaluation to decide which assets to trade. Because income in such a short period can be minimal, you may additionally choose to trade across a wide range of assets to strive and maximize your returns. That said, some would possibly completely trade the same pair for years.
This style is for sure a very active trading strategy. It can be extraordinarily profitable, however it carries with it a huge amount of risk. As such, day trading is normally better suited to experienced traders.
What is swing trading?
In swing trading, you’re still making an attempt to profit off market trends, however the time horizon is longer – positions are commonly held anywhere from a couple of days to a couple of months.
Often, your intention will be to identify an asset that appears undervalued and is likely to increase in value. You would buy this asset, then promote it when the fee rises to generate a profit. Or you can strive to locate overvalued property that are possibly to decrease in value. Then, you should sell some of them at a high price, hoping to buy them back for a lower price.
As with day trading, many swing traders use technical analysis. However, because their approach plays out across a longer period, crucial evaluation can also additionally be a valuable tool.
Swing trading tends to be a more beginner-friendly strategy. Mainly due to the fact it doesn’t come with the stress of fast-paced day trading. Where the latter is characterised by rapid decision-making and a lot of screen time, swing trading permits you to take your time.
What is position trading?
Position (or trend) trading is a long-term strategy. Traders buy property to hold for extended periods (generally measured in months). Their intention is to make a profit by selling these assets at a higher rate in the future.
What distinguishes position trades from long-term swing trades is the rationale behind placing the trade. Position merchants are involved with tendencies that can be found over prolonged intervals – they’ll attempt to profit from the basic market direction. Swing traders, on the other hand, generally are searching for to predict “swings” in the market that don’t necessarily correlate with the broader trend.
It’s not special to see position traders favor fundamental analysis, only because their time preference permits them to watch critical events materialize. That’s not to say technical evaluation isn’t used. While position traders work on the assumption that the trend will continue, the use of technical indicators can alert them to the opportunity of a trend reversal.
Like swing trading, position trading is an ideal strategy for beginners. Once again, the long time horizon gives them adequate opportunity to deliberate on their decisions.
What is scalping?
Of all of the techniques discussed, scalping takes place across the smallest time frames. Scalpers strive to game small fluctuations in price, frequently entering and exiting positions within minutes (or even seconds). In most cases, they’ll use technical evaluation to try and predict price movements and make the most bid-ask spread and other inefficiencies to make a profit. Due to the brief time frames, scalping trades regularly provide a small percentage of income – normally lower than 1%. But scalping is a numbers game, so repeated small profits can add up over time.
Scalping is by no means a beginner’s strategy. An in-depth perception of the markets, the systems you’re trading on, and technical evaluation are critical to success. That said, for merchants that comprehend what they’re doing, figuring out the proper patterns and taking benefit of short-term fluctuations can be distinctly profitable.
What is asset allocation and diversification?
Asset allocation and diversification are phrases that have a tendency to be used interchangeably. You would possibly know the principles from the saying don’t keep all your eggs in one basket. Keeping all of your eggs in one basket creates a central point of failure – the same holds true for your wealth. Investing your life financial savings into one asset exposes you to the same kind of risk. If the asset in question was the inventory of a specific business enterprise and that corporation then imploded, you’d lose your cash in one swift movement.
This isn’t just true of single assets, however of asset classes. In the case of a economic crisis, you’d anticipate all of the inventory you keep to lose value. This is due to the fact they’re closely correlated, which means that all have a tendency to observe the same trend.
Good diversification isn’t honestly filling your portfolio with thousands of special digital currencies. Consider an event where the world governments ban cryptocurrencies, or quantum computers break the public-key cryptography schemes we use in them. Either of these occurrences would have a profound impact on all digital assets. Like stocks, they make up a single asset class.
Ideally, you desire to unfold your wealth throughout a couple of classes. That way, if one is performing poorly, it has no knock-on impact on the relaxation of your portfolio. Nobel Prize winner Harry Markowitz brought this thought with the Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT). In essence, the idea makes the case for lowering the volatility and hazard related with investments in a portfolio by using combining uncorrelated assets.
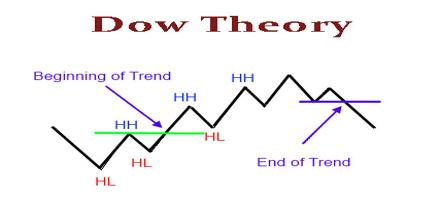
What is the Dow Theory?
The Dow Theory is a financial framework modeled on the ideas of Charles Dow. Dow established the Wall Street Journal and helped create the first US stock indices, known as the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA).
Though the Dow Theory was in no way formalized by Dow himself, it can be considered as an aggregation of the market ideas introduced in his writings. Here are some of the key takeaways:
Everything is priced in – Dow was a proponent of the efficient market hypothesis (EMH), the concept that markets replicate all of the available statistics on the charge of their assets.
Market trends – Dow is regularly credited with the very thinking of market tendencies as we understand them today, distinguishing between primary, secondary, and tertiary trends.
The phases of a primary trend – in primary trends, Dow identifies three phases: accumulation, public participation, and excess & distribution.
Cross-index correlation – Dow believed that a style in one index couldn’t be validated except it was observable in some other index.
The significance of volume – a trend must additionally be confirmed by high trading volume.
Trends are legitimate till reversal – if a trend is confirmed, it continues till a definite reversal occurs.
It’s really worth remembering that this isn’t an actual science – it’s a theory, and it may not hold true. Still, it’s a principle that stays vastly influential, and many traders and investors consider it an integral phase of their methodology.
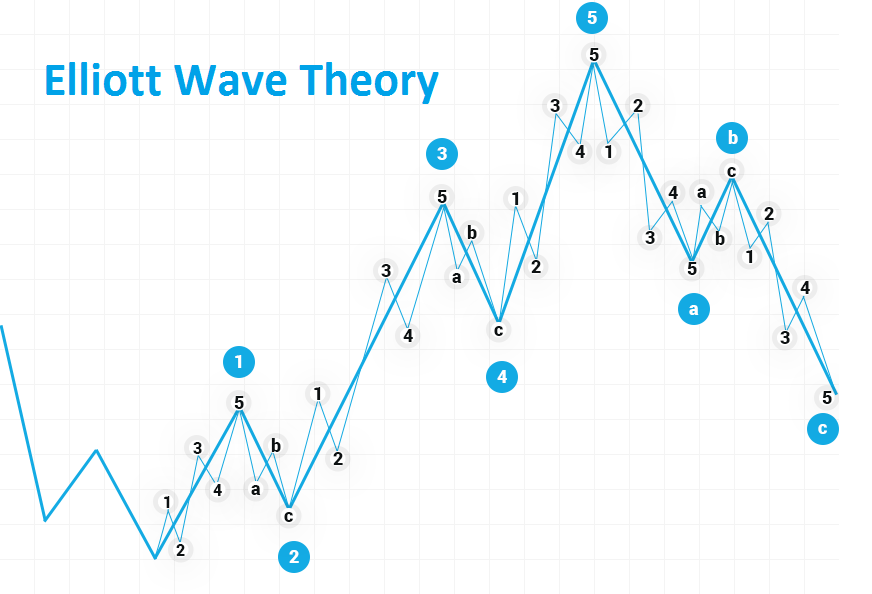
What is the Elliott Wave Theory?
Elliott Wave Theory (EWT) is a precept positing that market movements follow the psychology of market participants. While it’s used in many technical evaluation strategies, it isn’t an indicator or particular trading technique. Rather, it’s a way to analyze the market structure.
The Elliott Wave sample can commonly be identified in a collection of eight waves, each of which is either a Motive Wave or a Corrective Wave. You would have 5 Motive Waves that follow the common trend, and three Corrective Waves that move in opposition to it.
An Elliot Wave Cycle, with Motive Waves (blue) and Corrective Waves (yellow).
The patterns additionally have a fractal property, which means that you could zoom into a single wave to see another Elliot Wave pattern. Alternatively, you may want to zoom out to discover that the pattern you’ve been analyzing is also a single wave of a bigger Elliot Wave cycle.
Elliott Wave Theory is met with mixed reviews. Some argue that the methodology is too subjective due to the fact traders can pick out waves in a variety of ways without violating the rules. Like the Dow Theory, the Elliott Wave Theory isn’t foolproof, so it should not be considered as an genuine science. That said, many merchants have had great success by combining EWT with different technical evaluation tools.
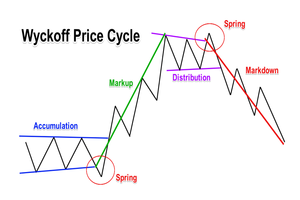
What is the Wyckoff Method?
The Wyckoff Method is an tremendous trading and investing approach that was developed by using Charles Wyckoff in the 1930s. His work is extensively viewed as a cornerstone of modern-day technical evaluation techniques throughout numerous financial markets.
Wyckoff proposed three vital laws – the law of supply and demand, the Law of Cause and Effect, and the Law of Effort vs. Result. He additionally formulated the Composite Man theory, which has big overlap with Charles Dow’s breakdown of primary trends. His work in this region is particularly treasured to cryptocurrency traders.
On the realistic side of things, the Wyckoff Method itself is a five-step strategy to trading. It can be broken down as follows:
Determine the trend: what’s it like now, and where is it headed?
Identify sturdy assets: are they moving with the market or in the opposite direction?
Find assets with ample Cause: is there enough reason to enter the position? Do the dangers make the potential reward really worth it?
Assess the possibility of the movement: do matters like Wyckoff’s Buying and Selling Tests factor to a possible movement? What do the charge and volume suggest? Is this asset ready to move?
Time your entry: how are the assets looking in relation to the accepted market? When is the best time to enter a position?
The Wyckoff Method was introduced nearly a century ago, however it stays fantastically relevant to this day. The scope of Wyckoff’s research was vast, and consequently the above must only be viewed as a very condensed overview. It’s encouraged that you discover his work in more depth, as it presents vital technical evaluation knowledge. Start with The Wyckoff Method Explained.
What is buy and hold?
The “buy and hold” strategy, possibly unsurprisingly, includes buying and retaining an asset. It’s a long-term passive play where buyers buy the asset and then leave it alone, regardless of market conditions. A precise instance of this in the crypto house is HODLing, which normally refers to traders that choose to purchase and preserve for years as a substitute of actively trading.
This can be an positive approach for those that decide upon “hands-off” investing as they don’t want to worry about temporary fluctuations or capital gains taxes. On the other hand, it requires patience on the investor’s phase and assumes that the asset won’t end up absolutely worthless.
If you’d like to read about an effortless way to follow this strategy to Bitcoin, take a look at out Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) Explained.
What is index investing?
Index investing ought to be considered as a form of “buy and hold.” As the name implies, the investor seeks to profit from the motion of assets inside a specific index. They should do so by buying the assets on their own, or via investing in an index fund.
Again, this is a passive strategy. Individuals can additionally gain from diversification across multiple assets, without the stress of active trading.
What is paper trading?
Paper trading could be any form of strategy – however the trader is only pretending to buy and sell assets. This is some thing you may think about as a novice (or even as an skilled trader) to test your competencies without placing your cash at stake.
You may additionally think, for instance, that you’ve found a excellent method for timing Bitcoin dips, and prefer to attempt profiting from these drops before they occur. But before you risk all of your funds, you may decide to paper trade. This can be as easy as writing down the price at the time you “open” your short, and again when you close it. You should equally use some sort of simulator that mimics popular trading interfaces.
The important advantage of paper trading is that you can check out strategies without losing your cash if things go wrong. You can get an idea of how your strikes would have carried out with zero risk. Of course, you want to be conscious that paper buying and selling solely offers you a constrained grasp of a actual environment. It’s difficult to replicate the actual emotions you experience when your cash is involved. Paper trading without a real-life simulator may additionally supply you a false feel of associated costs and fees, except you factor them in for specific platforms.
Binance affords a couple of choices for paper trading. For instance, the Binance Futures Testnet affords a full-fledged interface. If you’re building trading bots or programs yourself, then the spot exchange testnet can be accessed via API.